Safety, Occupational Health and Working Environment Management System of Chulalongkorn University consists of
(Reference: Chulalongkorn University Chemical Safety Board, Safety, Occupational Health and Environment Management System of Chulalongkorn University. Bangkok: Center for Safety, Health and Environment of Chulalongkorn University (SHECU), 2017)
Chulalongkorn University has adopted the concept of laboratory safety management as a result of the research project to raise safety standards in research laboratories in Thailand (Enhancement of Safety Practice of Research Laboratory in Thailand, ESPReL). The National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) support Chulalongkorn University as a leader in the operation. The Center of Excellence on Hazardous Substances and Waste Management and the Environmental Research Institute Chulalongkorn University developed a laboratory safety management system and tools considering the 7 elements, which later known as ESPReL and ESPReL Checklist. The tools can be used to independently explore and assess various hazards and risks. When the cause of the danger can be identified, the risk therefore can be precisely reduced. ESPReL Checklist is a tool that leads to the 7 relevant and interrelated elements of safety management as shown in the figure.
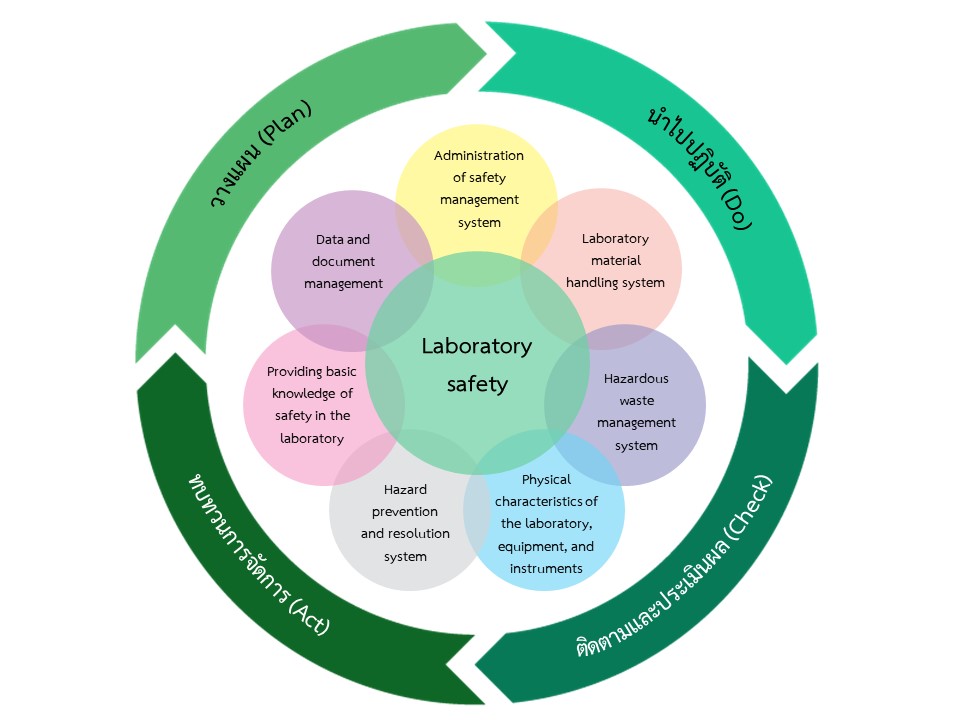
7 Key Elements of Security Management
Each element identifies the main risks in relation to other risks. Such elements include:
1. Administration of safety management system
Starting with university policies and safety programs, the policy and action plan are passed down to all levels of management in the same direction. But the details of the practice may be specific to the individual work. Roles, duties, and responsibility are clearly defined and can communicate the importance of having a management system in the form of documents, plans, reports, administrative structures, as well as, activities which can be used for human resource allocation, manpower and budget to support operations.
2. Laboratory material handling system
Preparing material inventories for chemicals, radioactive materials, biological substances for a good management system including information system, storage, transportation, and management of waste substances. Chulalongkorn University has provided ChemTrack & WasteTrack 2016 management kit for the users at all levels to be able access to accurate and up-to-date information about the substance which can be utilized for risk management, sharing chemicals, and budget allocation. For biological and radiological laboratories, they are also required to manage biological and radioactive material data to report according to the laws.
3. Hazardous waste management system
Approaches and management are consistent with the laboratory material handling system. Chulalongkorn University arranged ChemTrack & WasteTrack 2016 management kit for monitoring and tracking the movement of waste generated in laboratory. The laboratory shall classify hazardous waste according to the guideline, store in containers indicating type of waste, quantity, source and responsible person. Then, make an appointment with the admin to collect and send for disposal of by an authorized external agency. These data are then compiled into reports showing trends in waste generation, as well as, the cost of disposal of each segment.
4. Physical characteristics of the laboratory, equipment, and instruments
This includes architectural information, building characteristics (exterior and interior), room environment. Instruments and equipment are maintained and ready to use. Various engineering works such as structural work, electrical systems, sanitation and environment work, ventilation and air conditioning system, as well as, emergency system, emergency equipment, and communication system of the actual usage area, that facilitate safe operation in both normal and emergency conditions.
5. Hazard prevention and resolution system
There must be a risk management system based on real data in every aspect with a prioritized sequence of risk factors identification and risk assessment. Prevention plan and emergency response plan are prepared, establishing Safety practices, making an emergency plan, implementing the required procedures, drills, and equipment inspections in response to emergencies. The work section should have a clearly visible fire escape plan. Fire escape routes must be free from obstructions. There are warning signs, adequate personal protective equipment that are in working condition. There is a clear sequence for reporting incidents that linked to the central system of the university.
6. Providing basic knowledge of safety in the laboratory
The awareness must be raised and the necessary and appropriate knowledge must be provided for each target group with different roles including teachers, staff, researchers, students, cleaning staff, visitors, as well as, those who come to provide or receive services from time to time. There is an assessment and conditions for passing the assessment. The department should have a plan to educate personnel at all levels, have a system to assess the level of knowledge gained, and also have activities that will lead to the process of raising awareness. In addition to the courses for different groups of users, there are also courses for executives, safety board, as well as, a group of laboratory supervisors who work with chemicals, radioactive substances, biological substances
7. Data and document management
There must be a document management system relevant to the safe operation, which focuses on the system rather than on human. The workers must be able to understand and hand over the work when changing the responsible person. They can use it to extend knowledge in practice for continuous development of safety system. The level of responsibility is defined. The structure of the system for recording and storing information and documents includes document code, document name, document Type (Controlled - Uncontrolled), responsible person, owner, storage location, date of record. Updating the documents to the latest version and make them easy to access by storing in the form of document or electronic files, and have the main account of the documents.
(Reference: Chulalongkorn University Chemical Safety Board, Safety, Occupational Health and Environment Management System of Chulalongkorn University. Bangkok: Center for Safety, Health and Environment of Chulalongkorn University (SHECU), 2017)
In order to achieve tangible results from the operation, Chulalongkorn University employed the ESPReL safety concepts consisting of the 7 elements, and further developed it into the ESPReL management suite to used as a mechanism to collect, manage and process data from various elements. The ESPReL management suite contains laboratory data management system, laboratory materials information system coupled with Building Information Modeling (BIM), which is a physical data visualization system (Buildings and utilities components). The important tools including ESPReL/BSL/RS Checklists are used to survey the laboratory and collect data for each element online. The tools enable the users to see the condition of management and various risks by themselves. The results also show strengths and weaknesses in which the users can appropriately correct weaknesses to enhance the management of laboratory safety.
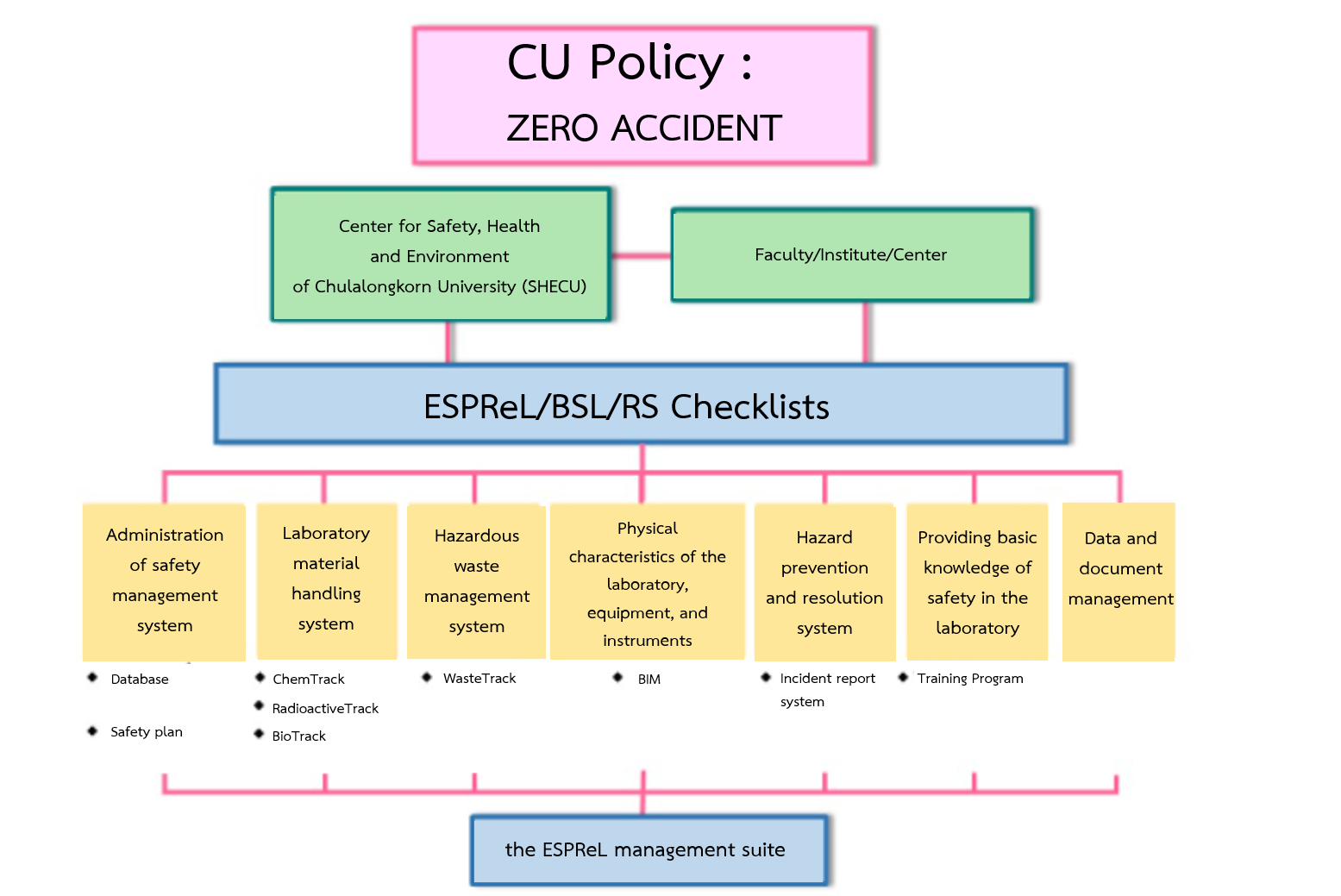
Driving mechanisms of safety, occupational health and environment management system
(Reference: Chulalongkorn University Chemical Safety Board, Safety, Occupational Health and Environment Management System of Chulalongkorn University. Bangkok: Center for Safety, Health and Environment of Chulalongkorn University (SHECU), 2017)
Laboratory data should provide an overview of the laboratory in terms of quantity, size, category, type of use (e.g., relevance to chemicals, radioactive materials, or biological substances), location of the laboratory (room number, floor, building), and overview at various levels (e.g., departments, faculties, university). The laboratory should regularly update the database to have up-to-date information.
Most laboratory materials are used for teaching, research and academic services. For example, chemicals, radioactive materials and biological substances. These materials are one of the major risk factors in the laboratory. Therefore, Up-to-date database and efficient information management systems are an important condition for risk management to increase work safety.
Data management system for chemical and hazardous waste
Chemical and chemical waste data management utilized ChemTrack & WasteTrack 2016 program. The users who want to use waste disposal service must register and input chemical data into the system. ChemTrack has a structure that can be used in chemical management such as
WasteTrack is able to record the data collected and track the movement of hazardous waste according to the specified criteria. Starting from the laboratory, waste is stored in a container that clearly indicates the type of waste, quantity, source and manufacturer of that waste. The responsible person makes an appointment to collect and send for disposal of by the authorized external agency. WasteTrack can report the waste, quantity, and disposal costs of each laboratory.
Data management system for radioactive materials and hazardous waste
Radioactive materials are a type of risk factor that requires data storage system for management, supervision, and inspection. In addition to the systems mentioned above, other relevant information should also be supervised, including:
Data management system for biological substances and hazardous waste
Information of biological substance management for use in safety supervision in various activities including
 |
Center for Safety, Health and Environment of Chulalongkorn University |
| Tel.: 0 2218 5222, 09 9132 6622 (official working hours) 09 9132 6622 (24-hour emergency response phone number) | |
| Email: shecu@chula.ac.th |
| Number of visitors | |||
|
|||
| 12 October 2019 |